You are actually paying heavily for your procratination, though you are unaware of the same. Procratination costa you heavily. Hence folllow the 9-proven steps to combat procratination.
3 - MAJOR PROBLEMS IN STEAM TURBINE CONDENSERS

The steam surface condenser is the largest heat exchanger in a power plant.
Hence the quality of the tubing within the condenser is critical for reliable operation of the plant.
Steam turbine condensers play a critical role in the efficiency and performance of power plants, particularly in steam power generation.
However, they are not without their challenges.
Here we will discuss THREE major problems often encountered with steam turbine condensers.
These problems, if allowed to grow into proportions, will eat away the profit of the Steam Turbine Power Plants.
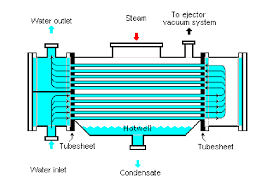
(Steam Turbine Condenser-Courtesy ResearchGate)
Fouling of condenser tubes (Water side fouling):
Fouling, or the accumulation of deposits on condenser surfaces, is a significant problem.
Fouling can occur due to the buildup of scale, sediment, or biological growth in the cooling water circuits.
This buildup insulates condenser tubes, reducing heat transfer rates and increasing condenser backpressure, which can impact turbine efficiency and power output.
The solution is to implement a ROBUST cooling Water (CW) chemical treatment.
In addition, long-term fouling deposits can increase tube corrosion by allowing corrosive chemical reactions to “hide” under the deposits.
Fouling can be subdivided into inorganic and organic causes.
Inorganic fouling is often composed of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate, but it can also be due to clay, and fine rock silt deposition.
In some cases, pieces of rotting or degrading cooling towers can become trapped within the condenser tubes or upon the surface of the tube sheet.
ACTIONS:
- Implement 3- shifts laboratory testing and deviations to be corrected.
- Calculate TTD (Terminal Temperature Difference) once per day and compare the deviation with designed one. Take actions to rectify problems.
- Calculate Heat Rate (HR) deterioration and take action.
- Implement OLTC (Online Tube Cleaning System). This will immensely help your condenser vacuum!!

(Steam turbine condenser fouling - Source IJSER)
Corrosion (Steam & Water side):
One of the primary challenges faced by steam turbine condensers is corrosion, which can result from various factors such as the presence of dissolved oxygen, impurities in the cooling water, or chemical reactions with materials used in construction.
Corrosion can lead to deterioration of condenser tubes, tube sheet, and other components, reducing heat transfer efficiency and increasing maintenance costs.
The most common contaminations in the condensed steam are gases are:
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Ammonia (from decomposing oxygen scavengers)
Condenser tube materials like stainless steels and titanium are resistant to these gases. However, copper-based alloys can be attacked by ammonia.
Admiralty brass and aluminium brass are the most susceptible to corrosive attack.
Pitting & Crevice corrosion are most common in the cooling water side of the condenser.
Pitting corrosion phenomenon is a highly localised attack and can produce through-wall penetration in very short order.
Failures may occur in less than four to five weeks in some cases.
In case of pitting corrosion, PH in a Pit can be as close to 2.0 in extreme cases.
Presence of chlorides in the condensate is very dangerous and initiate pitting at a faster rate.
ACTIONS:
- Implement 3- shifts laboratory testing and deviations to be corrected.
- TWICE A WEEK – Calculate Langelier Saturation Index (LSI). This will give you indication about corrosive attack.
- Maintain Good CW water chemistry.
- Maintain chloride level in the condensate within manufacturer’s limit.
Air Ingress leading to poor vacuum:
Air ingress into the condenser can lead to several major issues:
- Reduced vacuum levels.
- Decreased turbine efficiency,
- Potential damage to turbine blades due to erosion or corrosion.
- Increased back pressure in steam turbines.
Air leakage can occur through:
- Faulty seals.
- Damaged equipment.
- improper operation of air removal systems.
Effective air removal and sealing measures are essential to maintain optimal condenser performance.
If not attended, Heat Rate reduction will happen.
(Here post an image of air removal system of condenser or air ingress points in the condenser)
ACTIONS:
- Ensure that the air evacuation systems like Steam jet Ejectors or Vacuum pumps, are maintained properly and as per schedule.
- Conduct soap solution test on-load condition and identify leaking points and seal or prevent those.
- In extreme cases carry out Helium Leak Detection Test in the condenser.
PROCATIVE maintenance management system is the key of keeping the condenser performance at optimum level.
Finally, Cleanliness is profitability.
This MUST be the mantra of all power plant operators.
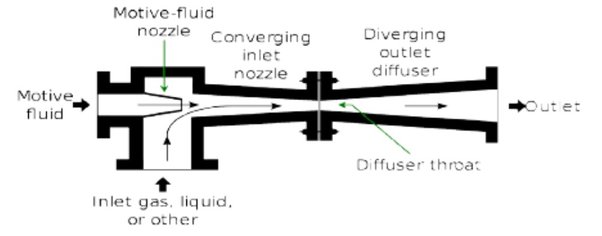
(Steam Turbine condenser air extraction Ejector system - Source Quora)

READ THeSe NEXT
Persons are always driven by finding happioness. But reality is neither happinees nor negetive situations, stay longer. People recover from both the situations in course of time. This is called HEDONIC ADAPTATION.
Here is a blog on Hedonic Adaptation.
Water crisis for India is loomimng large by 2025 to 20230. Not o0nly India this is going to affact whole world;s population. All nations must therefore take massive drive to sensitize all sections of people.
If not controlled, water security will be in danger.
